to Composites
to Ceramic Matrix Composites
Fabrication of Ceramic Matrix Composites by Polymer Infiltration and Pyrolysis (PIP)
Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich
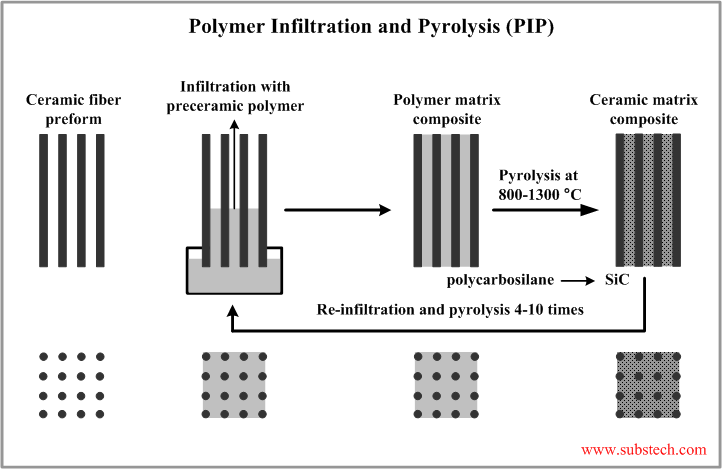
Polymer Infiltration and Pyrolysis (PIP) is the method of fabrication of Ceramic Matrix Composites comprising an infiltration of a low viscosity polymer into the reinforcing ceramic structure (e.g. fabric) followed by pyrolysis: heating the polymer precursor in the absence of oxygen when it decomposes and converts into a ceramic.
The Ceramics produced from polymers by pyrolysis are called polymer derived ceramics.
Preceramic polymers
Preceramic polymers (polymer precursors) are the Polymers, which can be converted into Ceramics by pyrolysis.
Molecules of preceramic polymers are commonly contain carbon (C) and/or silicon (Si) but may also contain nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), boron (B), aluminum (Al), titanium (Ti).
Polymer Infiltration and Pyrolysis (PIP) technique is used mainly for fabrication Composites with silicon carbide (SiC) matrices from polycarbosilanes (silicon derived polymer precursors): polymethylsilane (PMS) and allhydridopolycarbosilane. The yield of SiC of the precursors is about 65%.
Polysilazane may be converted into SiCN or Si3N4 with ceramic yield up to 90%.
Carbon matrices composites are fabricated by pyrolysis of either carbon thermosetting resins (phenolics, ruran resin, oxidized polystyrene, polyvinyl alcohol) or thermoplastic resins (pitches or coal tar). The carbon yield of these resins is 50-60%.
to top
Polymer Infiltration and Pyrolysis (PIP) process
- Fabrication of pre-impregnated material (prepreg). The reinforcing fibers are impregnated with a resin and then dried or cured to B-stage (partial curing). In such condition the viscosity of the polymer is increased and the prepreg may be shaped (laid-up).
- Lay-up. The prepreg is shaped by a tooling (mold).
- Molding. The laid-up prepreg is molded. Various molding methods may be used. In the bag molding a rigid lower mold is combined with a flexible upper mold (bag), which is pressed against the prepreg by either atmospheric pressure (vacuum bag mold) or increased air pressure (gas pressure bag mold). The pressurized preform is cured in an autoclave. A combination of a pressure with an increased temperature may also be achieved in compression molding.
- Infiltration of a preceramic polymer. The pores of the reinforcing structure are filled with a low viscosity solution of a preceramic polymer when the preform is immersed into it. The infiltration process is driven by the capillary forces therefore it is commonly conducted at normal pressure, however it may also be vacuum- or pressure-assisted.
- Pyrolysis. Pyrolytic decomposition of the preceramic polymer is performed in the atmosphere of Argon at a temperature in the range 1472-2372°F (800-1300°C). Nitride matrices (e.g. silicon nitride) are fabricated in the atmosphere of Nitrogen (N2) or Ammonia) (NH3). Volatile products such as CO, Hydrogen (H2), CO2, CH2, H2O are released as a result of pyrolysis forming a porous structure of the resulting ceramic matrix. The value of the ceramic yield is determined by the weight loss (amount of the released volatiles).
- Multiple re-infiltration and pyrolysis. The infiltration-pyrolysis cycle is repeated 4-10 times in order to decrease the residual porosity of the ceramic matrix.
Advantages and disadvantages of Polymer Infiltration and Pyrolysis (PIP)
Advantages of Polymer Infiltration and Pyrolysis (PIP):
- Fibers damage is prevented due to the processing at a relatively low temperature;
- Good control of the matrix composition and the microstructure;
- Reinforcing phase of different types (particulate, fibrous) may be used;
- Net shape parts may be fabricated;
- Matrices of various compositions (silicon carbide, silicon nitride, silicon carbonitride) may be obtained;
- No residual silicon is present in the matrix.
The disadvantages of the Polymer Infiltration and Pyrolysis (PIP):
- The fabrication time is relatively long due to the multiple infiltration-pyrolysis cycle;
- There is a residual porosity decreasing the mechanical properties of the composite;
- Relatively high production cost (higher than in Liquid Silicon Infiltration method).