SubsTech’s sister website Smooth Sliding provides independent engineering consulting services that help you to solve engine bearing related issues: failures, material selection, geometry design and optimization of hydrodynamic conditions.
Smooth Sliding is an engineering consulting company run by Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich:
- VP R&D of King Engine Bearings.
- World leading expert (32 years of experience) in design, technology and materials for Engine bearings in applications such as automotive, renewable energy, aviation, racing and others.
- Founder and owner of SubsTech (Substances & Technologies) – a leading professional website on Materials Science and Engineering.
- Author of numerous scientific and engineering publications and patents.
- Founder and owner of Smooth Sliding.
For further information and for requesting consulting services please visit our sister website Smooth Sliding.
to Metals
to Engine bearings
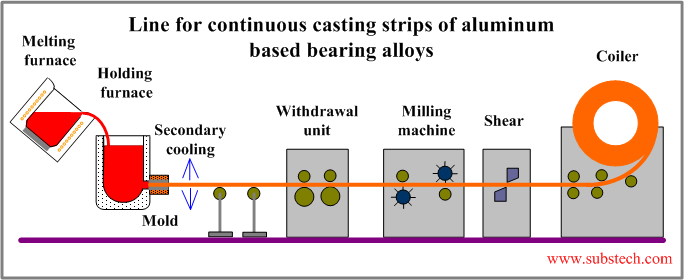
Continuous casting of aluminum based bearing alloys
Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich
Horizontal continuous casting methods are used for manufacturing Aluminum based bearing materials.
The alloys are cast in form of continuous strips (either cut-to-length or coiled). The aluminum casting is then cold rolled and backed with a steel strip in order to obtain bi-metal structure.
Casting of aluminum bearing alloys in short water-cooled graphite mold
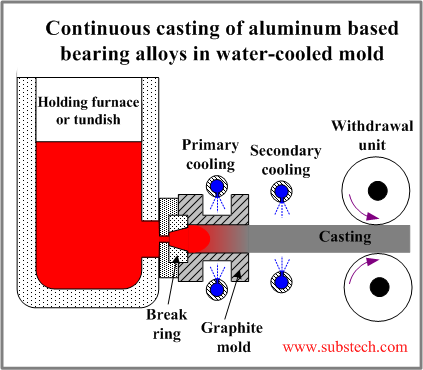
In this continuous casting method the mold surface is sprinkled by water streams.
This type of cooling is very effective due to elimination of air gap between the graphite mold surface and the coolers.
The process is terminated after casting 3-4 ton of aluminum based bearing alloys for replacing the graphite mold.
Benefits of casting in short water-cooled mold:
- Relatively high casting rate. High cooling rates achieved in the directly water-cooled Graphite mold allow to use short molds and reach relatively high withdrawal speeds.
- Non-intermittent withdrawal regime. Fast formation of thick and strong casting “skin” permit in many cases to pull the casting from the mold without pauses and reverse steps producing periodic non-homogeneous structure, which may cause cracks during cold rolling operation.
- Fine Grain structure. The resulted micro-structure of aluminum is fine with homogeneous distribution of tin, silicon particles and other constituents.
Disadvantages of casting in short water-cooled mold:
- Too thick defective surface layer, which should be machined (milled).
- Difficulties in coiling the cast strips caused by their high thickness. The castings are used in form of cut bars.
- High internal thermal stresses caused by fast cooling. The castings should be annealed prior to rolling;
- Longer rolling operation. More rolling passes is required to reduce high casting thickness to the final level.
- Inconvenient (open) water circulation system.
Casting of aluminum bearing alloys in submerged graphite mold
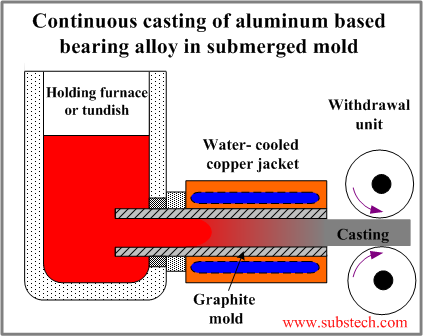
Graphite mold is cooled by water-cooled copper blocks. Cooling rate in this method is relatively low due to the air gap between the Graphite mold surface and the surfaces of the copper coolers. Molds of this type are longer than directly water-cooled graphite molds. The enter tip of the graphite mold is prominent into the holding vessel space and submerged into the melt.
Benefits of casting in submerged graphite mold:
- Relatively thin defective surface layer.
- Easy coiling. Relatively thin castings may be obtained.
- Fewer Rolling passes is required to reduce the lower thickness to the final level.
- Lower internal stresses. Moderate cooling and Solidification rates produce low internal stresses.
- Ability to stop and restart the casting process. The enter tip of the graphite mold is prominent into the holding vessel space and submerged into the melt. Such configuration allows to stop the withdrawal process for any time and then restart it. Solidification front stays within the mold.
- Closed cooling water system. Cooling water is circulating within the cooling blocks, which is more convenient and safer (a contact of molten aluminum with water is less possible).
Disadvantages of casting in submerged graphite mold:
- Non-homogeneous micro-structure. Thin and weak casting “skin” formed in the mold may tear due the friction with the graphite surface therefore casings solidified in molds with water-cooled copper coolers are withdrawn by an intermittent regime (with pauses and reverse steps) producing periodic non-homogeneous structure, which may cause cracks during cold rolling of low ductility alloys (eg. silicon containing alloys).
- Low casting rate.
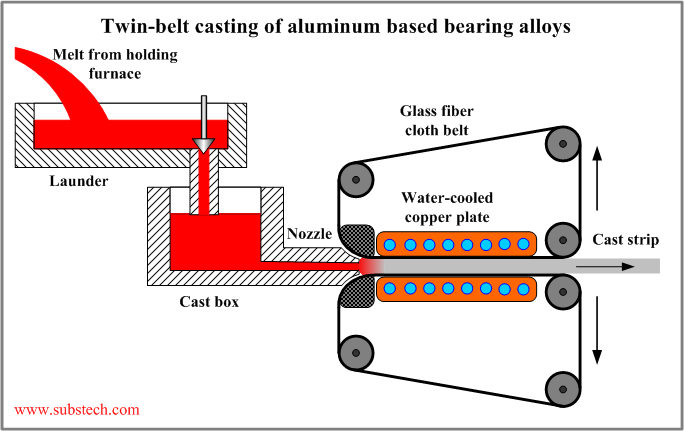
Twin-belt casting of aluminum based bearing alloys
Twin-belt casting relates to the continuous casting methods using traveling "endless" molds (rolls, belts, wheels). The method is characterized by zero relative movement between the mold (two belts) and casting surfaces.
Twin-belt casters are used for manufacturing cast strips of Aluminum based bearing materials.
In twin-belt casting process a melt is fed through a ceramic nozzle into the gap between two rotating endless thin belts held in tension.
The belts are supported and chilled by two water-cooled copper plate. The melt cools down and solidifies between the belts.
The cast strip is pulled out by a withdrawal unit synchronized with the drive of the belts.
Benefits of twin-belt casting:
- Surface machining is not required. Few surface defects form due to the absence of the relative movement of the belts and the solidifying alloy.
- High casting rate. The absence of tearing friction forces applied to the casting “skin” allows to increase the withdrawal rate.
- Low internal stresses. Low cooling rate produces low internal stresses.
- Non-intermittent withdrawal regime. No cracks form in the surface layer therefore pauses and reverse steps are not required in the withdrawal cycle (intermittent withdrawal regime produces periodic non-homogeneous structure, which may cause cracks during cold rolling operation).
- Easy coiling. Thin castings are obtained.
Disadvantages of twin-belt casting:
- Relatively coarse Grain structure caused by low cooling rate.
- Short service life of the belts.
- More expensive equipment as compared to the methods of casting in stationary molds.
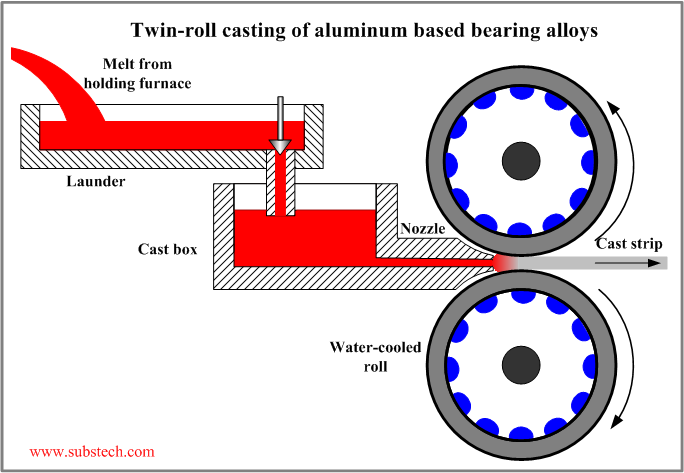
Twin-roll casting of aluminum based bearing alloys
Twin-roll casting relates to the continuous casting methods using traveling "endless" molds (rolls, belts, wheels). The method is characterized by zero relative movement between the mold (two rolls) and casting surfaces.
Twin-roll casters are used for manufacturing cast strips of Aluminum based bearing materials.
In twin-roll casting process a melt is fed through a ceramic nozzle into the gap between two rotating water-cooled rolls. The melt cools down and solidifies between the rolls. Additionally the solid strip exerts hot rolling with the thickness reduction of about 5-20%.
Sticking between the roll and the solidified strip is prevented by means of a parting agent applied to the roll surface. The agent contains Graphite or magnesium hydroxide.
Twin-roll casting process provides extremely high cooling rate up to 1000ºF/s (550ºC/s).
Benefits of twin-roll casting:
- Very fine Grain structure. High cooling rate results in very fine Grain structure of aluminum and homogeneous distribution of tin, silicon particles and other constituents.
- Surface machining is not required. Surface defects do not form due to negligible relative movement of the rolls and the solidifying alloy. The cast strips may be coiled and further processed (rolled) without surface machining (milling) in contrast to those cast in stationary molds (water-cooled graphite mold, submerged graphite mold).
- Very high casting rate. Extremely high cooling rate allows to increase the withdrawal rate to 40 inch/min (1000 mm/min).
- Non-intermittent withdrawal regime. No cracks form in the surface layer therefore pauses and reverse steps are not required in the withdrawal cycle (intermittent withdrawal regime produces periodic non-homogeneous structure, which may cause cracks during cold rolling operation).
- Easy coiling. Thin castings with a thickness of 0.24”/6 mm are obtained.
Disadvantages of twin-roll casting:
- Expensive equipment.
- Low casting thickness. It is more difficult to clad thin cast strips with pure aluminum.
- High internal thermal stresses caused by very fast cooling and solidification. The castings should be annealed prior to rolling.
Related internal links
to Metals
to Engine bearings