to Ceramics
to Carbon materials
Graphite
General information about graphite
Graphite is a crystalline, low density and soft allotrope of carbon.
Composition: Carbon
Color: Dark gray to black
Streak (color when crushed to a powder): Black gray
Luster: Metallic to dull
Crystal structure: Hexagonal
Cleavage: Basal in direction 1,1
Fracture: Conchoidal (smooth shell-like)
Density: 119 - 144 lb/ft³ (1.9*10³ - 2.3*10³ kg/m³)
Hardness: 1 - 2 Mohs
Melting temperature: about 6420°F (3550°C)
Name Origin: from the Ancient Greek graphein (to write).
Other distinctive characteristics:
- Stains fingers when touched;
- Feels greasy;
- Conducts electricity;
- Its flakes are thin, slightly flexible and inelastic brittle.
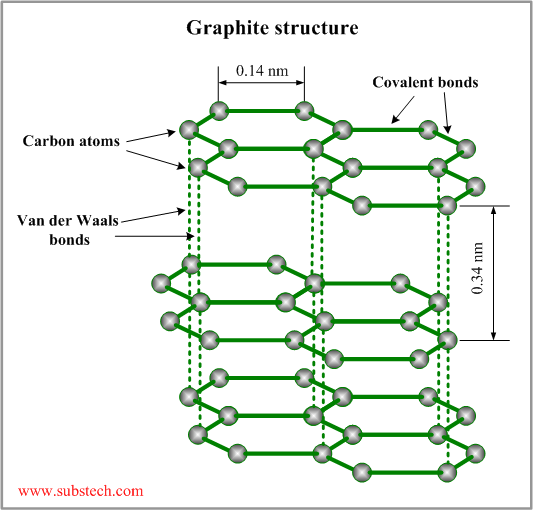
Graphite structure
The crystalline structure of graphite consists of hexagonal rings forming thin parallel plates (graphenes). Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to three other atoms in the plate (the angle between two bonds is 120°). The outermost electron shell of a carbon atom has four valence electrons, three of which are used by the covalent bonds. The forth valence electron does not take part in covalent bonds and may be easily displaced from the electron shell by an electric field. These elctrons provide electrical conductivity of graphite.
The graphenes are bonded to each other by weak Van der Waals forces. The layered structure of graphite allows sliding movement of the parallel graphene plates. Weak bonding between the plates determines softness and self-lubricating properties of graphite.
Graphite is rarely found in form of monocrystals. Most of graphite occurs in form of flakes or lumps. Graphite material having fine Grain structure is sometimes named amorphous graphite, however it is not really amorphous but microcrystalline.
to top
Classification of graphite
- Natural graphite
- Flake graphite. Flake graphite occurs mostly in metamorphic rocks (rocks that changed into another kind of rock) in form of small flat particles (flakes) of different sizes: from fine (50 μm diameter, 1 μm thick) to large (800 μm diameter, 150 μm thick). Due to the high degree of crystalline perfection of their structure graphite flakes have the values of the density, elctrical conductivity and thermal conductivity close to the theoretical maximum. Flake graphite possesses excellent compacting properties (low spring-back). Flake graphite contains 90-95% of carbon. Suppliers of flake graphite are China, Brazil, Canada, Norway, Madagascar, Ukraine, Zimbabwe.
- Vein graphite. Vein graphite (crystalline lump graphite) occurs as filling fissure (cracks in rocks) in veins in metamorphic or igneous (formed from molten magma or lava) rocks. Vein graphite may have various forms and dimensions from fine powder to lumps of 4” (10 cm) size. Vein graphite structure has high crystallinity, which provides excellent electrical conductivity of the material. Supplier of vein graphite is Sri Lanka.
- Microcrystalline (cryptocrystalline) graphite. Microcrystalline graphite (commercially called “amorphous”) occurs in metamorphic anthracite coal beds or in carbonaceous sedimentary rocks in form of extremely fine crystalline grains. Suppliers of microcrystalline (”amorphous”) graphite are China, Mexico, Korea, Zimbabwe.
- Synthetic graphite
- Primary synthetic graphite. Prymary synthetic graphite is made from mixtures of petroleum coke and coal tar pitch. The carbon containing mixture is heated in the absence of Oxygen at temperatures 4530 - 5430°F (2500 - 3000°C). Under these conditions amorphous carbon transforms to crystalline graphite. Primary synthetic graphite has a high purity: more than 99.5% of carbon.
- Secondary synthetic graphite. Secondary synthetic graphite is recovered from machining operations of graphite parts, graphite scrap, defective and broken graphite details. Secondary synthetic graphite has lower crystallinity and lower purity than primary product.
- Graphite fibers. Fabrication of graphite fibers is based on pyrolysis (chemical decomposition by heat in the absence of oxygen) of polymer precursor fibers. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN), rayon, pitch, coal tar or petroleum asphalt may be used as precursor materials. Pyrolysis results in transformation of the precursor polymer material to graphite, crystal layers of which are linked in bundles oriented along the the fibers. The resulting graphite fibers are extremely anysotropic (mechanical strength in fibers direction is much higher than in other directions). Graphite fibers are used for manufacturing Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites.
Graphite properties
- High melting temperature;
- Low density (28% of steel);
- Low hardness;
- Electrical conductivity highest of non-metallic materials;
- High thermal conductivity;
- High thermal shock resistance;
- High strength (particularly compressive strength), which increases with the temperature rise;
- High stiffness (modulus of elasticity);
- High thermal resistance. Graphite is capable to work in the temperature range from absolute zero to 6330°F (3500°C) in inert atmosphere.
- High chemical and corrosion resistance;
- Good oxidation resistance. Graphite starts to be oxidized in oxidizing atmosphere at 932°F (500°C).
- Low absorption coefficient for X-rays.
- High resistance to neutron radiation. Graphite slows down fast neutrons and scatters thermal neutrons.
- High radiation emissivity;
- Ability to absorb radio waves;
- Low wettability by liquid metals;
- Good machinability;
- Ability to absorb Gases.
Graphite properties determine the variety of the areas of its applications in industry, transport, energetics, defence, medicine, science.
to top